1. Phase correlation
1. Phase correlation
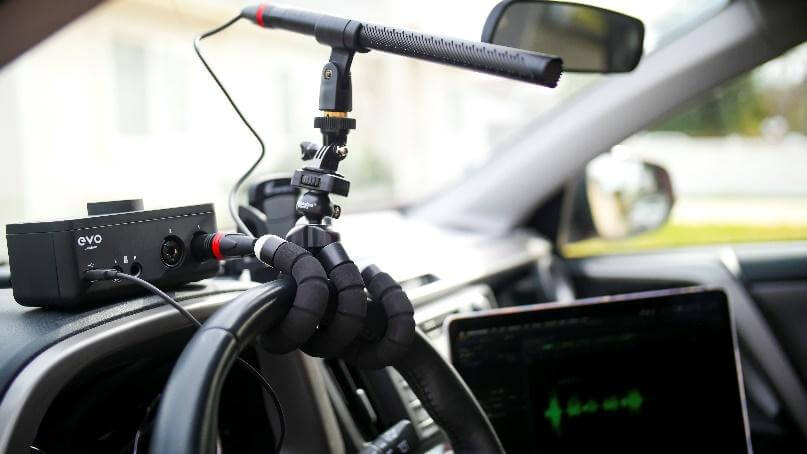
Phase correlation between mics is HUGELY important when on the quest for the elusive ‘perfect guitar tone’. If you need more than one mic to accomplish that sound, here is a trick I do to check phase coherency.
Connect a reamp box to the amplifier you are recording. Using your DAW, send a side snare or stick click (anything with an enhanced attack transient) out through your DAW via the reamp box and into the amp. Record your mics capturing this sound, then have a look at the waveforms to see how close they are. My starting procedure is to get the mics’ respective waveforms to all start at the exact same time, then go on from there. It takes some time to get it dead on, but the results justify the time and effort!
2. Get a great monitor mix before tracking
2. Get a great monitor mix before tracking
When tracking guitars, context is everything. It’s difficult to achieve great starting tones and takes if the drum (and bass if already tracked) mix is lacklustre. I personally like to get a decent sounding monitor mix while tracking, which not only helps show up any issues if the tone isn’t cutting it, but also inspires the artist who’s playing.
3. Guitar Picks matter
A trick I use a lot is having guitarists try different guitar picks to alter the tone, intensity and feel of a part. Sometimes using a softer pick can even out dynamics or take away some harshness. Similarly, if a part is lacking power and articulation, a harder or sharper pick could help add some attack.
4. Change setups when double tracking
4. Change setups when double tracking
When creating big and wide sounding guitar tracks, layering different tones is a huge part of how I do it. I generally like to start with double tracked rhythm guitars on the same guitar and amp (panned hard left and right), then each layer after that (lead guitars, octave parts, cleaner parts etc) will be done with either a different amp, guitar or both. This helps create a different frequency response for each layer and can help provide separation and clarity in the mix.
5. Know your amps/speakers
5. Know your amps/speakers
Understanding how the volume of the amp can affect how the amp and cab reacts is also useful when tracking guitars. All valve amps will have a point at which the output tubes start saturating, and this can either be a good or bad thing for the tone you are looking to achieve. Similarly, all guitar cabs will have a point where they start resonating in an unpleasant way, or where the speakers become over worked. However, with too little output, sometimes it can sound a bit thin and brittle. It’s critical to know the limits of the cab you are recording to maximise the tone you are looking to create. Don’t forget the room and environment the cab is being recorded will interact at higher volumes too!
Our Products
-

2in | 2out Audio Interface
-

10in | 6out Audio Interface
-

10in | 14out Audio Interface
-

20in | 24out Audio Interface
-

24in | 32out Audio Interface
-
2in | 2out Audio Interface
-

4in | 4out Audio Interface
-

24in | 24out Audio Interface
-

Everything you need to start recording
-

8 Channel Smart Preamp with AD/DA
-

8 Channel Mic Pre & ADC
-

8 Channel Mic Pre + Tone Control
-
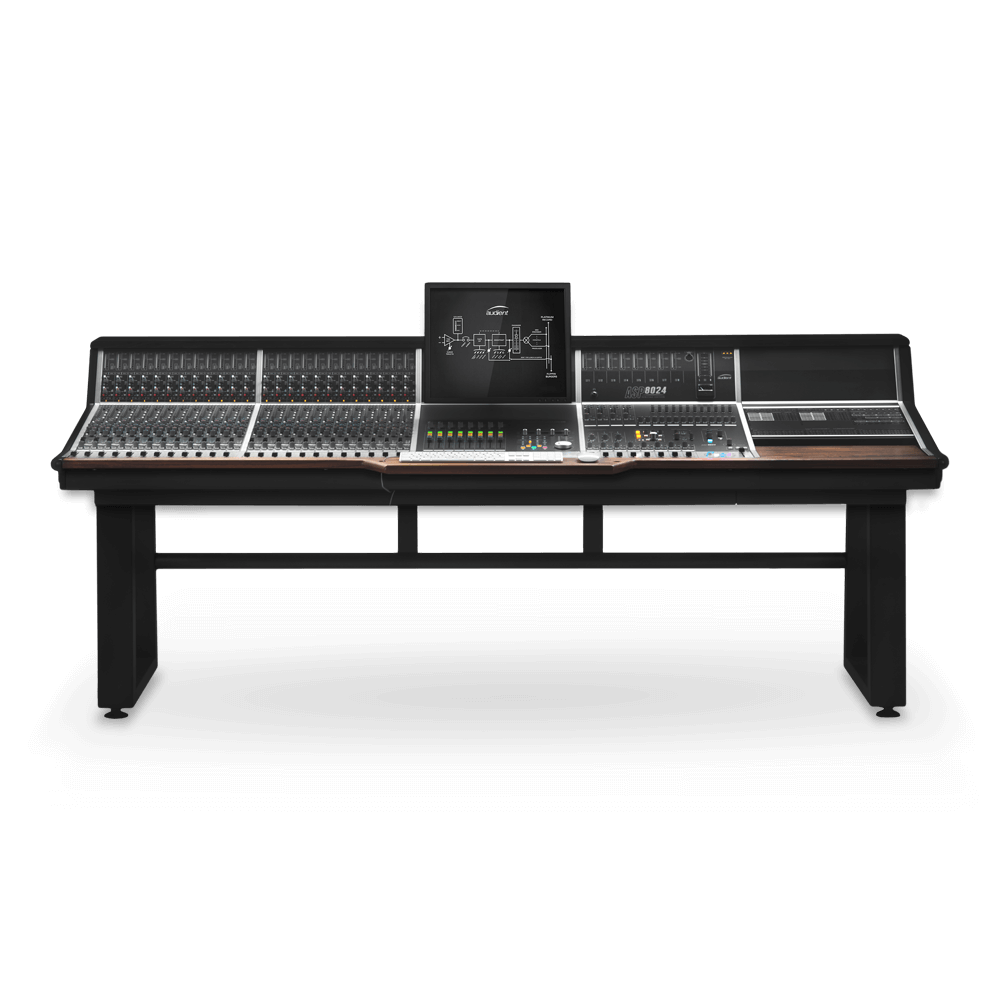

Modular Analogue Recording Console
-

Small Format Analogue Recording Console
-

Small Format Analogue Recording Console
-
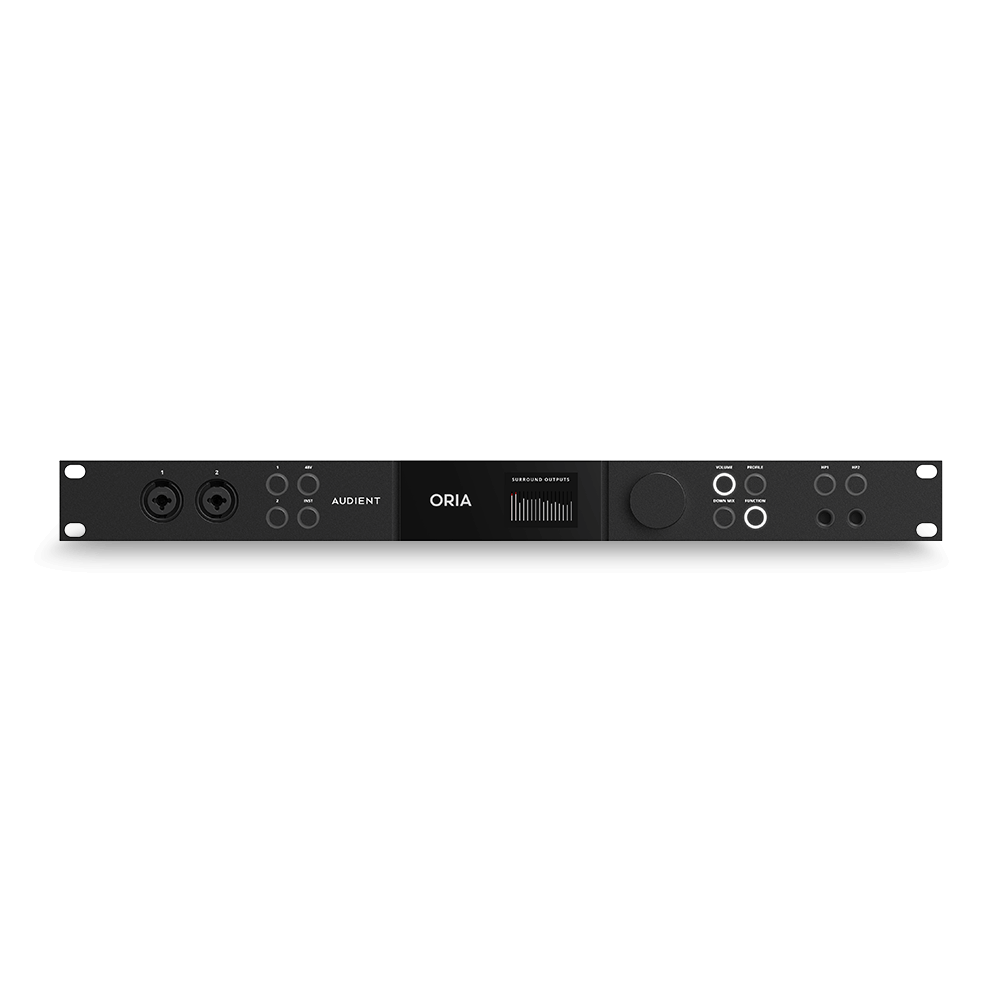

Immersive Audio Interface and Monitor Controller
-

Desktop Monitor Controller


